As businesses increasingly embrace the cloud for their infrastructure needs, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has emerged as a leading cloud service provider, offering a scalable and flexible platform for organizations of all sizes. However, the migration to the cloud brings new security challenges that demand careful consideration and proactive measures. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of AWS security, exploring the fundamental practices, robust features, and best-in-class solutions to protect your AWS environment from potential vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
Understand Shared Responsibility Model
Before diving into specific AWS security features, it’s crucial to grasp the shared responsibility model. AWS follows a shared responsibility model, which means that while AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, customers are accountable for securing their data, applications, and operating systems. By comprehending this model, organizations can better allocate security responsibilities and implement suitable measures to safeguard their assets.
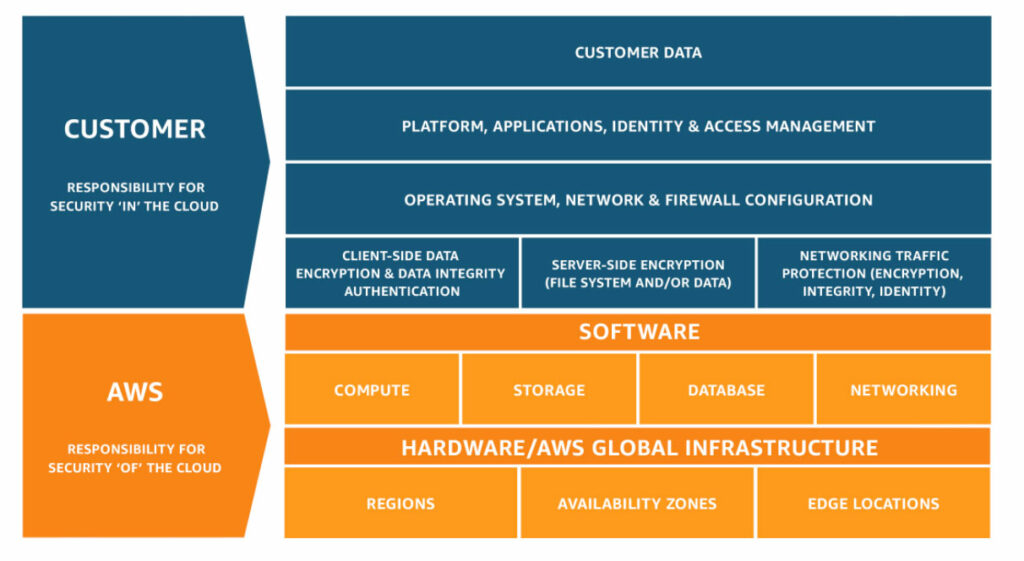
More details can be found at: AWS Shared Responsibility Model
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is the foundation of AWS security, enabling organizations to manage user access and permissions effectively. By implementing least privilege principles, organizations can grant users the minimum necessary access required to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. IAM also facilitates multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an extra layer of security, making it harder for malicious actors to compromise user accounts.
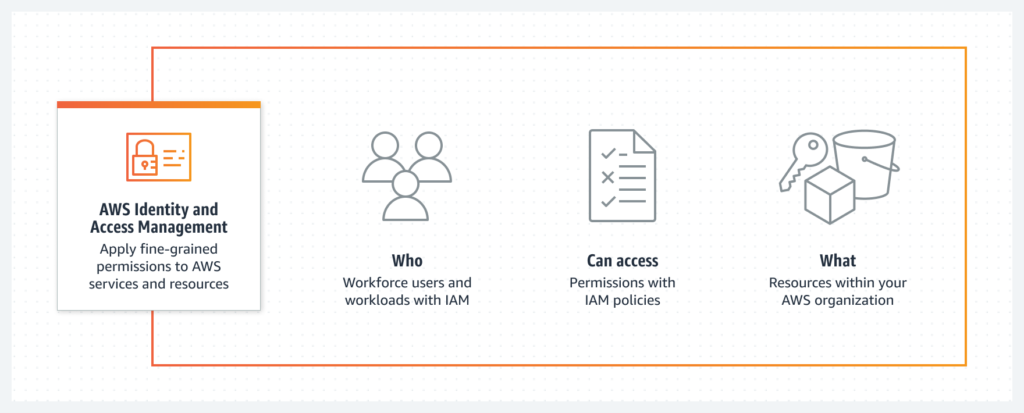
More details can be found at: AWS IAM Documentation
Secure Data Storage with S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a scalable and cost-effective storage solution widely used for data storage and backup. Securing data in S3 involves setting up access controls through bucket policies and Access Control Lists (ACLs). AWS provides encryption options, such as server-side encryption (SSE) and client-side encryption, to protect data at rest and in transit. Regular audits and monitoring of S3 access logs contribute to a robust data security posture.
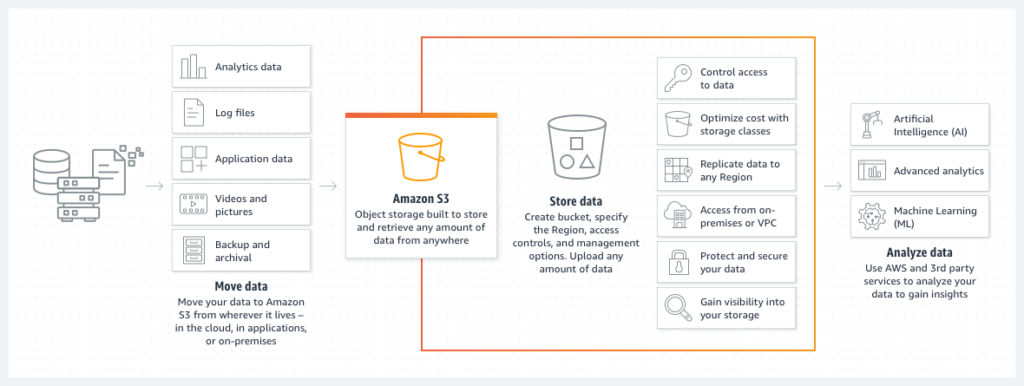
More details can be found at: AWS S3 Security
Network Security with VPC
The Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows organizations to create a private network within the AWS cloud, offering enhanced control over network security. Configuring security groups and network access control lists (NACLs) enables fine-grained control of inbound and outbound traffic. VPC also supports Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections and AWS PrivateLink for secure communication between VPCs and on-premises resources.
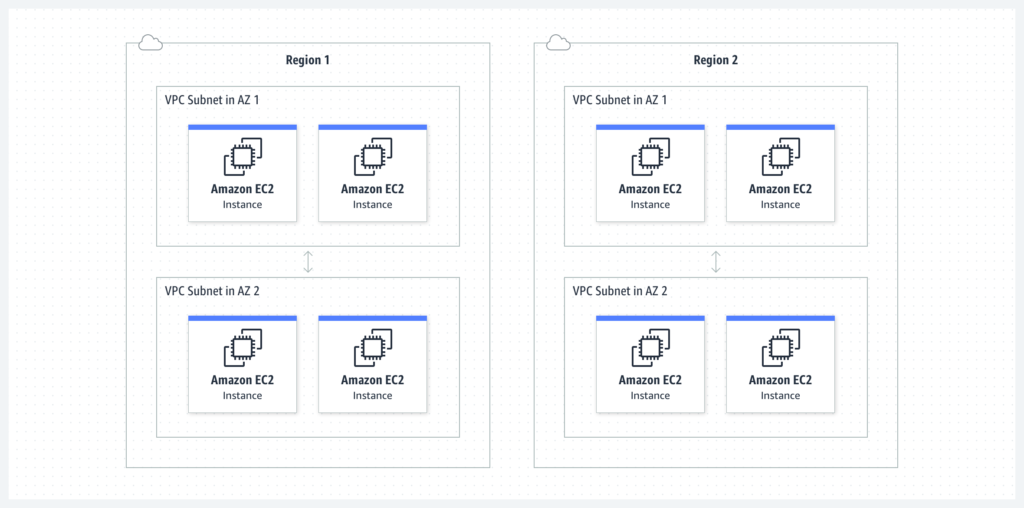
More details can be found at: AWS VPC Documentation
DDoS Protection with AWS Shield
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can disrupt AWS resources and impact business continuity. AWS Shield provides essential DDoS protection, automatically safeguarding against common attack vectors. AWS Shield Standard is available to all AWS customers at no additional cost, while AWS Shield Advanced offers more advanced protection with 24/7 support and real-time attack visibility.
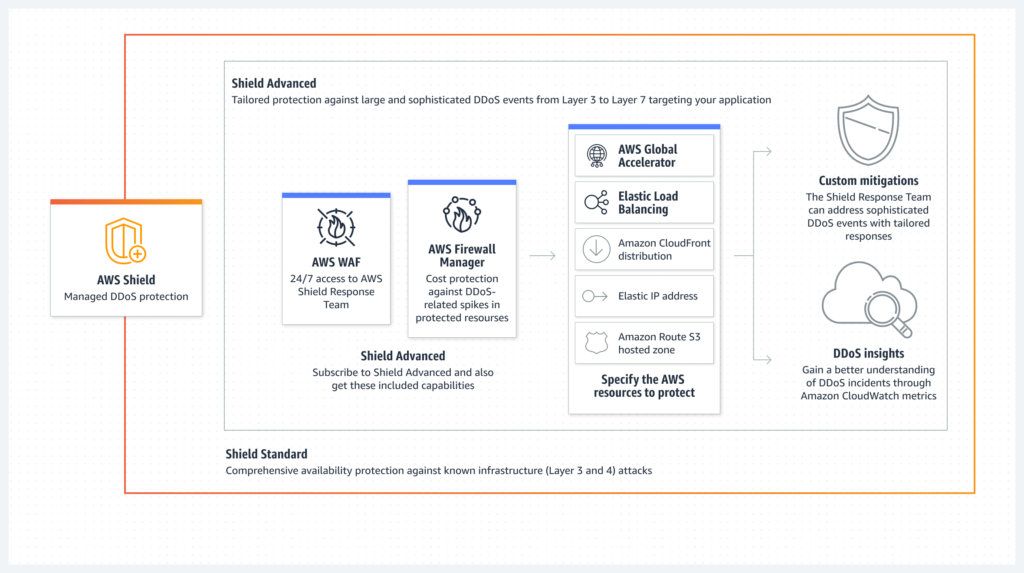
More details can be found at: AWS Shield Overview
Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Implementing robust monitoring and logging practices is vital to detect and respond to potential security incidents promptly. AWS CloudTrail captures API activity, providing a detailed audit trail for monitoring account activity. Amazon CloudWatch allows organizations to collect and track metrics, set alarms, and gain insights into AWS resource utilization. Integrating these services with AWS Config helps maintain compliance and assess resource configurations for security best practices.
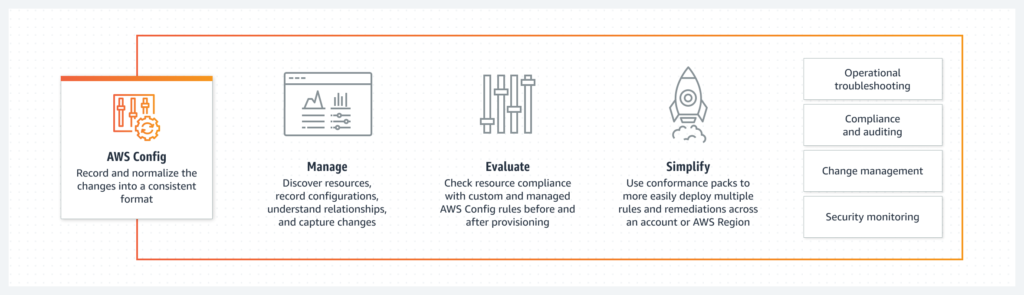
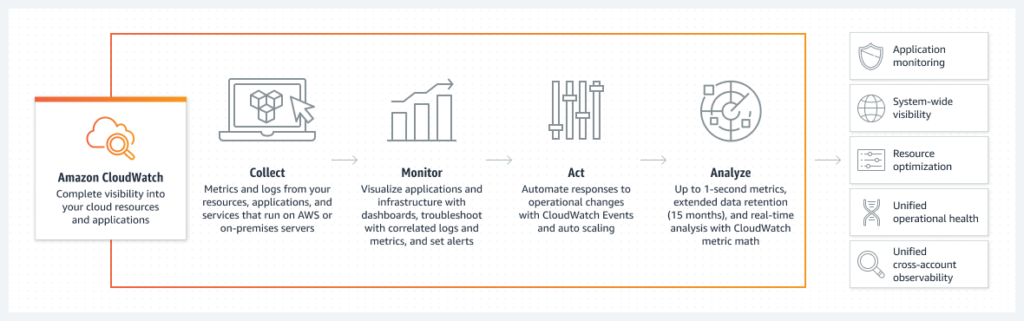
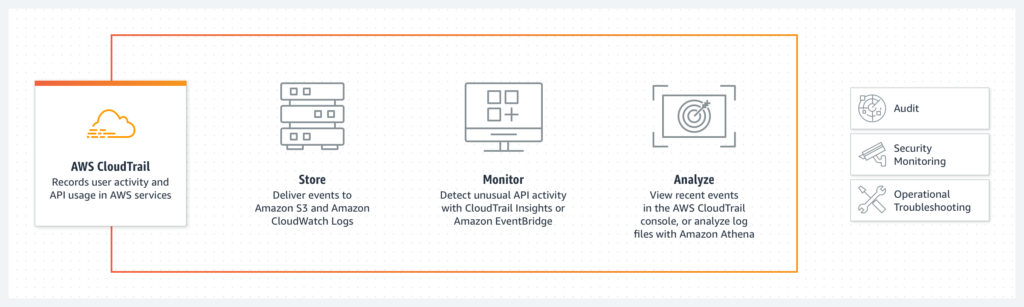
More details can be found at: AWS CloudTrail, Amazon CloudWatch, AWS Config
Conclusion
Protecting your AWS infrastructure from potential threats and breaches is of paramount importance in today’s digital landscape. By understanding the shared responsibility model and implementing best practices for identity and access management, secure data storage, network security, DDoS protection, and continuous monitoring, organizations can create a robust and secure cloud environment on AWS.
Remember, AWS security is an ongoing process, and staying updated with the latest security features and best practices is crucial. By leveraging the comprehensive security offerings from AWS and maintaining a proactive security posture, businesses can confidently embrace the cloud while keeping their data and applications safe from potential cyber threats.
If you are in need of help configuring or setting up any of these services please feel free to reach out to us, it’s what we do all day every day. Contact Us
